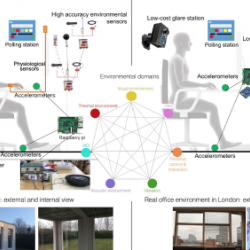
This project aimed to create a toolkit for capturing occupant satisfaction with their environment in buildings in order to feed the next generation of smart buildings with a more holistic set of metrics for comfort and enjoyment of a space. The toolkit consists of a range of existing sensors and additional devices that together capture the wide effects of novel resource‐efficient technologies, such as the user responses to automatic façade systems and the effects of material‐efficient structures on occupant productivity and wellbeing.
Outcomes
The project produced the Building Impulse Toolkit (BIT), which enables active and passive user feedback and analyses these factors in relation to the thermal, acoustic and other factors in the space. This will help establish the basis of more unobtrusive tracking of occupant satisfaction that can drive automated changes to the environment.
Method
Prototyping
Next Steps
More work is needed on passive metrics that do not rely on any manual input from people, and technologies that utilise them. There is also social research needed into the ethics and social acceptability of passive metrics in the built environment.